SparkSQL and JDBC Connection
SQL command is one of the most widely-used languages to query data from databases. SparkSQL allows user to use SQL commands to process data in Spark as if the data were stored in a database. SparkSQL will transform any SQL commands into Spark’s RDD operations. With Spark’s Thrift server, any JDBC compatible clients can submit SQL queries to SparkSQL.
In this section, we create a Spark cluster with Thrift server. Then, show how to use a JDBC client, beeline, to manipulate and query data.
Launch a Spark cluster with Thrift server
Follow this guide to launch a Spark cluster.
Then, click on Scale to add a superset node which has Thrift installed.
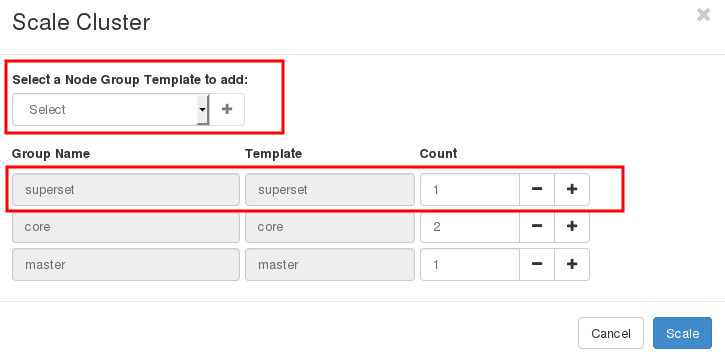
This node also has Apache Superset, a data visualization tool which can connect to Thrift server via JDBC connection. If interested, see an example of Thailand Government Spending for a guideline to use SparkSQL with Superset.
Note the IP of the superset node which we will use it to login to the node in the next step.
Login to the node and download sample data
Login to the superset node by using the IP address of the node.
$ ssh centos@IP_OF_SUPERSET
[centos@test-superset-0 ~]$
Run the following commands to download sample data. The sample data is from UCI bank dataset.
[centos@test-superset-0 ~]$ wget http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/00222/bank.zip
[centos@test-superset-0 ~]$ unzip bank.zip
[centos@test-superset-0 ~]$ hdfs dfs -put bank-full.csv /user/centos
The sample data looks like:
"age";"job";"marital";"education";"default";"balance";"housing";"loan";"contact";"day";"month";"duration";"campaign";"pdays";"previous";"poutcome";"y"
58;"management";"married";"tertiary";"no";2143;"yes";"no";"unknown";5;"may";261;1;-1;0;"unknown";"no"
44;"technician";"single";"secondary";"no";29;"yes";"no";"unknown";5;"may";151;1;-1;0;"unknown";"no"
Submit queries with beeline
Connect beeline to Thrift server. Suppose that the superset node is named test-superset-0. we set the connection string to
jdbc:hive2://localhost:10000
Set the username to centos. The password is ignored by default.
[centos@test-superset-0 ~]$ beeline
Beeline version 1.2.1.spark2 by Apache Hive
beeline> !connect jdbc:hive2://localhost:10000
Connecting to jdbc:hive2://localhost:10000
Enter username for jdbc:hive2://localhost:10000: centos
Enter password for jdbc:hive2://localhost:10000:
18/08/01 16:48:08 INFO Utils: Supplied authorities: localhost:10000
18/08/01 16:48:08 INFO Utils: Resolved authority: localhost:10000
18/08/01 16:48:08 INFO HiveConnection: Will try to open client transport with JDBC Uri: jdbc:hive2://localhost:10000
Connected to: Spark SQL (version 2.3.1)
Driver: Hive JDBC (version 1.2.1.spark2)
Transaction isolation: TRANSACTION_REPEATABLE_READ
0: jdbc:hive2://localhost:10000>
Then, type the following SQL commands in beeline.
CREATE DATABASE bank;
USE bank;
CREATE TABLE bank
USING csv
OPTIONS (header 'true', inferSchema 'true', delimiter '\073', mode 'FAILFAST')
LOCATION '/user/centos/bank-full.csv';
SELECT age, count(1) FROM bank GROUP BY age ORDER BY age;
+------+-----------+--+
| age | count(1) |
+------+-----------+--+
| 18 | 12 |
| 19 | 35 |
| 20 | 50 |
| 21 | 79 |
... skip ...
Note that beeline cannot parse ; (semicolon) in SQL command correctly. So we replace it with ascii code \073.
Type Ctrl-D to exit from beeline.